Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (21): 3412-3419.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.21.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Phase II study on surface construction and biocompatibility of polymer materials as cardiovascular devices: surface construction and biological responses
Chen Bao-lin1, Wang Dong-an 2, 3
- 1 Bureau of Scientific Research, Hulunbuir College, Hulunbuir 021008, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
2 Institute of Polymer Science, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, Zhejiang Province, China
3 Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, Tennessee 38163, USA
-
Online:2014-05-21Published:2014-05-21 -
About author:Chen Bao-lin, Professor, Bureau of Scientific Research, Hulunbuir College, Hulunbuir 021008, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Bao-lin, Wang Dong-an. Phase II study on surface construction and biocompatibility of polymer materials as cardiovascular devices: surface construction and biological responses[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(21): 3412-3419.
share this article
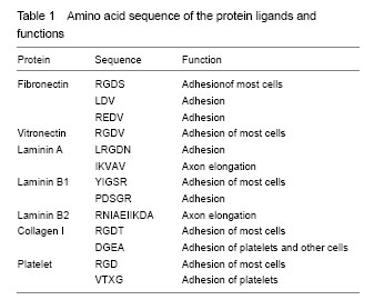
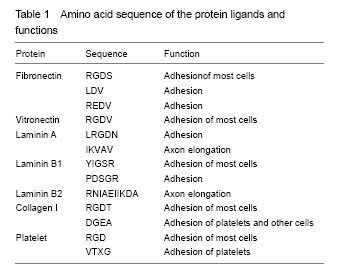
Protein adsorption Proteins that are widespread and abundant in the living body fluids are the main substance of the organism. Meanwhile, they are also one of the major information carriers of biometric identification. Therefore, protein adsorption on the surface of polymer biomaterials is crucial for the surface biocompatibility of materials[17]. Thermodynamic mechanism underlying interactions between proteins and polymer surface is first based on the hydrophilic-hydrophobic interaction. In view of the hydrophobicity of polymer surface and water as well as the hydrophilicity of proteins that is bound between the water and polymer surface, proteins in the aqueous solution inevitably move to the polymer surface to “separate” the polymer materials from the water, and thereby, the surface energy of the polymer materials is reduced. In addition, the original hydrogen-bond interaction between the water and polymer surface is weak, that is, the hydrogen bond between water molecules on the polymer surface does not significantly interfere with the polymer surface. Therefore, these water molecules show a relatively regular arrangement because of their own hydrogen-bond interaction. When the proteins implement the separation of water from the polymer surface, the presence of relatively hydrophilic proteins will disrupt the hydrogen-bond interaction on the polymer surface and thereby cause the irregular arrangement of water molecules, which can result in a substantial increase of entropy in the system. Consequently, protein adsorption on the polymer surface will become inevitable, and the trend of protein adsorption will be more obvious along with the increasing of hydrophobization degree on the polymer surface. Secondly, the interaction between the polymer surface and proteins is based on electrical action. Proteins mostly have negative charges, and therefore, the stronger the positive charge on the polymer surface, the more obvious the tendency of protein adsorption is. Certainly, we cannot rule out the impact of side groups of proteins carrying positive charges. Almost all proteins in an aqueous solution have a three-dimensional structure, which is closely related to the interactions between the same solvents of proteins. In addition, the protein conformation is also associated with the polar force, dispersion forces and the role of disulfide bonds inside the protein chain. However, varying degrees of protein inactivation are inevitable during the process of protein adsorption. Specifically, the hydrophobic side chain of the protein in the aqueous solution is folded inside the molecular chain[18], and when placed on the polymer surface, these hydrophobic side chains are bound to eversion, they cause the irreversible substantial change in protein conformation[19]. Given the irreversible protein adsorption, the dynamic properties of this process appears to be particularly important. The results show that when the polymer material is in contact with the blood, of all the serum proteins, albumin that has the maximum content in serum is the fastest to arrive at the polymer surface, and it is always preponderant during the process of protein adsorption because of its fastest speed. In consequence, albumin action often plays a decisive role in the irreversible protein adsorption on the polymer surface. Biometric identification during cell adhesion Cell adhesion in vivo or on the synthetic surface should be complete through the interaction between proteins and cell surface receptors. Three typical cell adhesion receptors are integrins, proteoglycans and selectins on cell surface[20]. However, in tissue engineering, specific receptors are generally not involved in the studies concerning cell/material interaction, but checked by asialoglycoprotein. In contrast to cell surface receptors, there is a large amount of soluble protein ligands in human body fluids[21], including fibrinogen, fibronectin, thrombospondin, vitronectin, and some forms of von Willebrand factor. While others, such as collagen, laminin, and von Willebrand factor with high molecular weight, only exist in the the extracellular matrix of cross-linking macromolecules. Cells have a strong ability to reconstruct their extracellular matrix[22], which may synthesize or secrete proteins and also can remove the proteins by hydrolysis method. The cross-linking of proteins should be realized by enzymes (mainly glutamyltranspeptidase) that can develop the reaction between the carboxyl group on the side chain of aspartic acid or glutamic acid and amino group on the side chain of adjacent lysine to generate a amide bond[23]. The amino acid sequence of the protein ligands and function are listed in Table 1[24]."

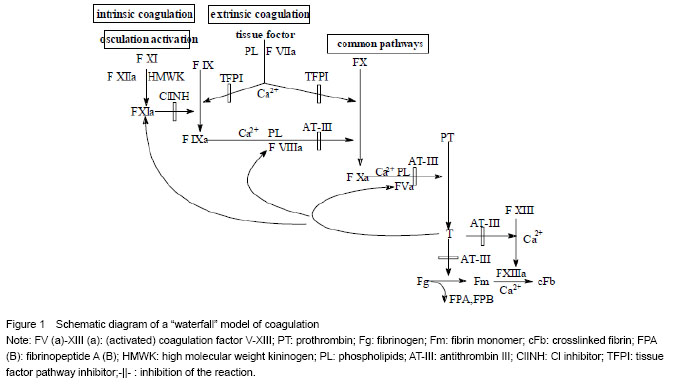
“Waterfall” model of enzyme catalysis during coagulation and fibrinolysis The waterfall model of enzyme catalysis is a very common model used to describe the biological chain reactions in the human body. The process of activating a “waterfall” is that zymogen is transformed into enzyme, and this process is often triggered by another “waterfall” process. There are three “waterfall” models closely related to biocompatibility of biomaterials, that is, the “waterfall” models of coagulation, fibrinolysis and complement[25-28]. The waterfall model of coagulation is formed depending on independent and co-existence of many kinds. The specific process is shown in Figure 1. Surface construction of biomaterials and protein adsorption on the surface The basic method of regulating protein adsorption on the polymer surface is based on the hydrophilization of polymer surface[29-33]. Surface modification of hydrophilic polymer using surface grafting method By introducing the hydrophilic polymer to the substrate surface of the biomaterials, the surface passivation can be achieved mainly via surface grafting and in situ polymerization. These methods include conventional chemical grafting method, photochemical method, radiation and electrochemical method. Among these methods, graft polymerization is a relatively mature method, and the typical product is polyurethane modified by grafting polymerization of polyacrylamide[34]. On this polymer surface, blood compatibility is increased along with the increasing grafting density. Another typical product is produced by UV-irradiation that can graft polyethylene glycol methacrylate onto the substrate surface of polyethylene terephthalate materials in the presence of photosensitizers. This product is likely to present with comb-like surface, on which, the polymer content can reach micron level[35]. In addition, polyethylene glycol can be synthesized with diisocyanate to form new polyurethane derivatives by chemical grafting method[36-37]. Based on this, the copolymers of polyethylene glycol grafted at sulfonic acid end groups are proved to be the heparinoids. Compared with those with –OH end groups, the coagulation time of these copolymers is two times as long as that of those with –OH end group, while seven times longer than that of unmodified polyurethane. Unexpectedly, the amount of adsorbed fibrinogen is little higher than that of polyethylene glycol derivates with –OH, but both of these two copolymers only have 50% the amount of adsorbed fibrinogen of unmodified polyurethane. This example also shows that to enhance the antithrombogenicity is not just to reduce the protein adsorption on the polymer surface. In another experiments, low grafting density is often encountered when the polymer surface is modified by surface grafting of water-soluble polyethylene glycol or polysaccharide to obtain hydrogel surface, but the grafting density is precisely critical[38-40]. The problem seems to be solved by plasma multilayer grafting and/or grafting of high molecular weight polyethylene glycol[41-42]. Another approach is the use of highly-branched polyethylene glycol or microsphere electrophoresis[43-44]. So far, it has been reported that polyethylene glycol at a sufficient grafting density is successfully introduced into the surface of polytetrafluoroethylene using plasma multilayer grafting[45]. These facts indicate that grafting methods and chemical properties of the reactants are equally important, moreover, the surface grafting is not the best means for surface modification. Surface modification of hydrophilic polymer using surface adsorption Another surface modification method for hydrophilic polymer is the surface adsorption of amphiphilic molecules. The advantages are: in situ preparation and usage of aqueous medium; easier to obtain high fixed density of modifiers compared to chemical grafting method. During the chemical grafting process, the grafting reaction become more difficult when the grafting density is increasing, because of steric repulsion of molecular chains of the modifiers. Conversely, during the surface adsorption of amphiphilic molecules, a low-energy surface can maximize the surface density of surfactant molecules. Additionally, the surface stability can be modified in a variety of covalent bonding, or by other methods after the completion of surface adsorption, such as plasma irradiation and radiation irradiation method. Comparison of surface grafting and surface adsorption is performed on polyurethane materials, one for the surface fixation of polyethylene glycol by hydrogen addition reaction with Polyurethane urethane, and the other for absorption of the ABA-type amphiphilic copolymer containing poly-hydroxyethyl methacrylate and polystyrene on the polyurethane surface using solution method[46]. The results show that the blood compatibility of the graft-modified surface has no improvement, but that of the absorption-modified surface is significantly improved, indicating surface modification is decided by the surface fixation density of modifiers rather than the chemical properties of poly-hydroxyethyl methacrylate and polyethylene glycol. Because of their protein resistance and platelet adhesion, PEO with end groups and polysaccharide have been widely used[47-50], in particular the surface modification of polyethylene glycol with phosphorylcholine groups[51-55]. Surface modification of hydrophilic polymer using self-assembly method Based on the surface absorption of amphiphilic molecules, surface supramolecular systems have also been greatly developed, which include amphiphilic self-assembling systems, chemisorption system, multi-layer system and nano-structure system. Such supramolecular systems can be used to construct two-dimensional and three-dimensional surface structure in the absence of a covalent bond. Amphiphilic self-assembly: two typical examples of amphiphilic self-assembly are self-assembled monolayer modification of liposome surface using polyethylene glycol with end groups[56-57], and LB film self-assembled modification of hydrophobic glass using multi-segmented copolymers of polyethylene glycol and bisphenol[58-59]. The experiment has confirmed that the blood compatibility of the two modified surfaces have been significantly improved. Chemisorption system: Self-assembly modification which is based on the chemisorption principle is mainly used in metal or ceramic surfaces. Considering the high affinity between thiol and gold, the most common system is to introduce the molecular chain with thiol groups into the gold surface so as to form a stable, dense and ordered self-assembled structures[60-66]. Multi-layer self-assembly system: Multi-layer self-assembly system is usually prepared by alternating self-assembly of polyelectrolyte layers with negative charges. The typical application example is the famous polylysine-alginate coacervate model. Alginate carries negative charges, and polylysine serves as a polycation substance. Calcium alginate can form a gel in the calcium-contained medium, and then polylysine adhere to this surface due to electrical effects. This process is repeated to form a multilayer isotropic coacervate[67]. This multi-layer self-assembly system can be available to prepare microcapsules for cell transplantation. If the copolymer of polyethylene glycol and poly-lysine forms, the products from the above-mentioned process become more immunologically inert[68]. On this basis, the light polymerization is used to deal with alginate gel, in order to obtain a more stable microcapsule structure[69]. Of course, the multi-layer self-assembly system of copolymers carrying positive-negative charges can be also expanded to polyion multilayer structure applications[70]. Body modification of the substrate based on hydrophilic polymer Body modification of the substrate based on hydrophilic polymer involves three aspects, that is, phase separation of materials, relationship between mechanical properties and biocompatibility, interaction between the molecular weight of materials and the component of materials. Firstly, for example, the basic method of body modification for polyurethane biomaterials is blending. Under such conditions, the addition of hydrophilic polymers such as polyethylene glycol will inevitably lead to phase separation of materials followed by surface microdomains, thus affecting the adsorption behavior of surface proteins that include the component ratio and the adsorption state, which ultimately affects the biocompatibility of materials[71-79]. To clarify the relationship between the mechanical properties and biocompatibility of the materials, polyvinyl alcohol is selected for example. Studies have shown that the mechanical properties and biocompatibility of the material often show a negative relationship. The degree of crosslinking, which is related to both mechanical properties and biocompatibility to some extent, is dominantly crucial for body crosslinking using glutaraldehyde to strengthen the mechanical properties[80-82]. As for the third problem, the final biocompatibility of materials not only depends on the chemical properties of the hydrophilic polymers, but also closely relates to the molecular weight and the bonding chemical properties, but also with the closely related to the molecular weight and the bonding of the surface and the substrate[83]. In addition to a variety of surface construction methods mentioned, the further regulation of surface protein absorption is also important for tissue engineering materials, in order to achieve a surface protein ratio for adhesion of a certain kinds of cells. We can firstly rule out the majority of proteins by non-specific rejection on the surface of hydrophilic polymers, and then introduce bioactive factors to selectively distinguish a or several certain kinds of proteins, hereby to achieve the specific recognition of a particular cell."
| [1]Boretos JW, Eden M. Contemporary Biomaterials: material and host response, clinical applications, new technology, and legal aspects. Park Ridge, NJ: Noyes Publications, 1984: 232-233. [2]Chen BL, Wang DA. Surface construction and biocompatibility of polymeric used for cardiovascular medical device. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2013;17(34):6183-6292. [3]Chen BL, Wang DA. Hemocompatibility of biomedical polymeric materials Design of anticoagulant materials. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(34): 6393-6396. [4]Chen BL, Wang DA. Preparation and mechanism of anticoagulatent biomedical polymer materials with blood compatibility. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(29):5507-5510. [5]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Investigation on methods of surface modification of tissue engineering materials: Polymer surface group transformation and bioactive molecule immobilization. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(3):552-554. [6]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Surface modification of tissue-engineered materials Plasma and grafting modification. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(3):587-590. [7]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Application of polymer biomaterials in the tissue engineering. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(6): 1189-1192. [8]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Polymer porous membrane prepared using thermally induced phase separation. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;11(40):8217-8219. [9]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Topology of tissue engineered material surface for cell compatibility. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;11(18): 3653-3656. [10]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Effects of physical-chemical properties of tissue engineered material surface on cell compatibility. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2007;11(1):197-200. [11]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Cytological effect of tissue engineering materials with cell compatibility. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu. 2006;10(45):225-227. [12]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX, et al. The application of biomedical tissue engineering and the polymer tissue engineering material. Gaoshi Like Xuekan. 2007;27(1):24-26. [13]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX, et al. Study on the blood compatibility of biomedical ploymer materials--project of antithromboeicity materials. Suihua Xueyuan Xuebao. 2007;27(1):186-188. [14]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Study on surfaces modify of the tissue engineering materials and application in the tissue engineering. Hulunbeier Xueyuan Xuebao. 2007;15(1):52-54. [15]Chen BL, Wang DA, Feng LX. Study on the tissue compatibility of biomedical ploymer materials--project of tissue-compatibility materials. Hulunbeier Xueyuan Xuebao. 2006;14(6):34-36. [16]Wang DA, Chen BL, Ji J, et al. Selective adsorption of serum albumin on biomedical poiyurethanes modified by a poly(ethylene oxide)coupling-polymer with cibacron blue(F3G-A) end groups. Bioconjug Chem. 2002;13(4): 792-803. [17]Peppas NA, Langer R. New challenges in biomaterials. Science. 1994; 263(5154):1715-1720. [18]Horbett TA, Lew KR. Residence time effects on monoclonal antibody binding to adsorbed fibrinogen. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 1994;6(1):15-33. [19]Chinn JA, Posso SE, Horbett TA, et al. Postadsorptive transitions in fibrinogen adsorbed to polyurethanes: changes in antibody binding and sodium dodecyl sulfate elutability. J Biomed Mater Res. 1992;26(6):757-778. [20]Hynes RO. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992;69(1):11-25. [21]Buck CA, Horwitz AF. Cell surface receptors for extracellular matrix molecules. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:179-205. [22]Singer II, Scott S, Kawka DW, et al. Cell surface distribution of fibronectin and vitronectin receptors depends on substrate composition and extracellular matrix accumulation. J Cell Biol. 1988;106(6):2171-2182. [23]Mosher DF. Assembly of fibronectin into extracellular matrix. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1993;3(2):214-222. [24]Yamada KM. Adhesive recognition sequences. J Biol Chem. 1991;266(20):12809-12812. [25]Brown EJ. Complement receptors, adhesion, and phagocytosis. Infect Agents Dis. 1992;1(2):63-70. [26]Remes A, Williams DF. Immune response in biocompatibility. Biomaterials. 1992;13(11):731-743. [27]Esmon CT. Thrombomodulin as a model of molecular mechanisms that modulate protease specificity and function at the vessel surface. FASEB J. 1996;9(10):946-955. [28]Plow EF, Herren T, Redlitz A, et al. The cell biology of the plasminogen system. FASEB J. 1995;9(10):939-945. [29]Jeon SI, Lee JH, Andrade JD, et al. Protein—surface interactions in the presence of polyethylene oxide: I. Simplified theory. J Colloids Interf Sci. 1991;142(1):149-158. [30]Jeon SI, Andrade JD. Protein—surface interactions in the presence of polyethylene oxide: II. Effect of protein size. J Colloids Interf Sci. 1991;142(1):159-166. [31]Milton Harris J. Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Chemistry: Biotechnical and Biomedical Applications. New York: Plenum Press, 1992: 385. [32]Llanos GR, Sefton MV. Does polyethylene oxide possess a low thrombogenicity? J Biomater Sci Polymer Ed. 1993;4(4): 381-400. [33]Amiji M, Park K. Surface modification of polymeric biomaterials with poly(ethylene oxide), albumin, and heparin for reduced thrombogenicity. J Biomater Sci Polymer Ed. 1993;4(3):217-234. [34]Fujimoto K, Tadokoro H, Ueda Y, et al. Polyurethane surface modification by graft polymerization of acrylamide for reduced protein adsorption and platelet adhesion. Biomaterials. 1993;14(6):442-448. [35]Uchida E, Uyama Y, Ikada Y. Grafting of Water-Soluble Chains Onto a Polymer Surface. Langmuir. 1994;10(2): 481-485. [36]Han DK, Ryu GH, Park DK, et al. Adsorption behavior of fibrinogen to sulfonated polyethyleneoxide-grafted polyurethane surfaces. J Biomater Sci Polymer Ed. 1993;4(5): 401-413. [37]Freij–Larsson C, Wesslén B. Grafting of polyurethane surfaces with poly(ethylene glycol). J Biomater Sci Polymer Ed. 1993;50(2):345-352. [38]Shoichet MS, Winn SR, Gentile FT, et al. Poly(ethylene oxide)-grafted thermoplastic membranes for use as cellular hybrid bio-artificial organs in the central nervous system. Biotech Bioeng. 1994;43(7):563-572. [39]Li S, Chatelier RC, Zientek P, et al. Covalent surface attachment of polysaccharides via bifunctional epoxides. Abstr Paper Am Chem Soc. 1995;209:305. [40]Gombotz WR, Guanghui W, Horbertt TA, et al. Protein adsorption to poly(ethylene oxide) surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res. 1991;25(12):1547-1562. [41]Merrill EW. Poly(ethylene oxide) star molecules: synthesis, characterization, and applications in medicine and biology. J Biomater Sci Polymer Ed. 1993;5(1-2):1-11. [42]Bergstrom K, Osterberg E, Holmberg K, et al. Effects of branching and molecular weight of surface-bound poly(ethylene oxide) on protein rejection. J Biomater Sci Polymer Ed. 1994;6(2):123-132. [43]Van Alstine JM, Burns NL, Riggs JA, et al. Electrokinetic characterization of hydrophilic polymer coatings of biotechnical significance. Colloid Surfaces. A. 1993;77(2): 149-158. [44]Burns NL, van Alstine JM, Harris JM. Poly(ethylene glycol) grafted to quartz: analysis in terms of a site-dissociation model of electroosmotic fluid flow. Langmuir. 1995;11(7): 2768-2776. [45]López GP, Ratner BK, Tidwell CD, et al. Glow discharge plasma deposition of tetraethylene glycol dimethyl ether for fouling-resistant biomaterial surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res. 1992;26(4):415-439. [46]Nojiri C, Olano T, Koyanagi H, et al. In vivo protein adsorption on polymers: visualization of adsorbed proteins on vascular implants in dogs. J Biomater SciPolym Ed. 1992;4(2):75-88. [47]Lee JH, Kopecek J, Andrade JD. Protein-resistant surfaces prepared by PEO-containing block copolymer surfactants. J Biomed Mater Res. 1989;23(3):351-268. [48]Amij MM, Park K. Analysis on the surface adsorption of PEO/PPO/PEO triblock copolymers by radiolabelling and fluorescence techniques. J Appl Polym Sci. 1994;52(4): 539-544. [49]Moghimi SM, Muir IS, Illum L, et al. Coating particles with a block co-polymer (poloxamine-908) suppresses opsonization but permits the activity of dysopsonins in the serum. Biochimicaet Biophysica Acta. 1993;1179(2):157-165. [50]Cinni E, Cavedagna D, Falsone G, et al. Numerical and functional modifications in platelets induced by polyester coated by a hydrophilic polymer. Biomaterials. 1993;14(8): 588-590. [51]Marchant RE, Yuan S, Szakalasgratzl G. Interactions of plasma proteins with a novel polysaccharide surfactant physisorbed to polyethylene. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 1994;6(6):549-564. [52]Ishihara K, Hanyuda H, Nakabayashi N. Synthesis of phospholipid polymers having a urethane bond in the side chain as coating material on segmented polyurethane and their platelet adhesion-resistant properties. Biomaterials. 1995;16(11):873-879. [53]Terlingen JG, Feijien J, Hoffman AS. Immobilization of surface active compounds on polymer supports using a gas discharge process. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 1992;4(1):31-33. [54]Tseng YC, Mcpherson T, Yuan CS, et al. Grafting of ethylene glycol-butadiene block copolymers onto dimethyl-dichlorosilane-coated glass by gamma-irradiation. Biomaterials. 1995;16(13):963-972. [55]Amiji M, Park K. Surface Modification by radiation-induced grafting of PEO/PPO/PEO triblock copolymers. J Colloid Inter Sci. 993;155(1):251-255. [56]Lasic DD. Sterically stabilized vesicles. Angew Chem. 1994;33:1685-1698. [57]Woodle MC, Lasic DD. Sterically stabilized liposomes. Biochimicaet Biophysica Acta. 1992;1113(2):171-199. [58]Cho CS, Kotaka T, Akaike T. Cell adhesion onto block copolymer Langmuir-Blodgett films. J Biomed Mater Res. 1993;27(2):199-206. [59]Uchida M, Tanizaki T, Oda T, et al. Control of surface chemical structure and functional property of Langmuir-Blodgett film composed of new polymerizable amphiphile with a sodium sulfonate. Macromolecules. 1991;24(11):3238-3243. [60]Lopez GP, Albers MW, Schreiber SL, et al. Convenient methods for patterning the adhesion of mammalian-cells to surfaces using SAMs of alkanethiolates on gold. J Am Chem Soc. 1993;115(13):5877-5878. [61]Prime KL, Whitesides GM. adsorption of proteins onto surfaces containing end-attached oligo (ethylene oxide): a model system using self-assembled monolayers. J Am Chem Soc. 1993;115(23):10714-10721. [62]Dimilla PA, Folkers JP, Biebuyck HA, et al. Wetting and protein adsorption of self-assembled monolayers of alkanethiolates supported on transparent films of gold. J Am Chem Soc. 1994;116(5):2225-2226. [63]Löfås S. Dextran modified self-assembled monolayer surfaces for use in biointeraction analysis with surface plasmon resonance. Pure Appl Chem. 1995;67(5):829-834. [64]Osterberg E, Bergstrom K, Holmberg K, et al. Protein-rejecting ability of surface-bound dextran in end-on and side-on configurations: comparison to PEG. J Biomed Mater Res. 1995;29(6):741-747. [65]Ferguson GS, Chaudhury MK, Biebuyck HA, et al. Monolayers on disordered substrates: self-assembly of alkyltrichlorosilanes on surface-modified polyethylene and poly(dimethylsiloxane). Macromolecules. 1993;26(22): 5870-5875. [66]Silver JH, Hergenrother RW, Lin JC, et al. Surface and blood-contacting properties of alkylsiloxane monolayers supported on silicone rubber. J Biomed Mater Res. 1995; 29(4):535-548. [67]O'Shea GM, Sun AM. Encapsulation of rat islets of Langerhans prolongs xenograft survival in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 1986;35(8):943-946. [68]Sawhney AS, Hubbell JA. Poly(ethylene oxide)-graft-poly (L-lysine) copolymers to enhance the biocompatibility of poly(L-lysine)-alginate microcapsule membranes. Biomaterials. 1992;13(12):863-870. [69]Desai NP, Sojomihardjo A, Yao Z, et al. Interpenetrating polymer networks of alginate and polyethylene glycol for encapsulation of islets of Langerhans. J Microencapsul. 2000;17(6):677-690. [70]Ishihara K, Inoue H, Kurita K, et al. Selective adhesion of platelets on a polyion complex composed of phospholipid polymers containing sulfonate groups and quarternary ammonium groups. J Biomed Mater Res.1994;28(11): 1347-1355. [71]Silver JH, Myers CW, Lim F, et al. Effect of polyol molecular weight on the physical properties and haemocompatibility of polyurethanes containing polyethylene oxide macroglycols. Biomaterials. 1994;15(9):695-704. [72]Lelah MD, Cooper SL. Polyurethanes in Medicine. Raton, Florida: CRC Press, 1986:225. [73]Brunstedt MR, Ziats NP, Robertson SP, et al. Protein adsorption to poly(ether urethane ureas) modified with acrylate and methacrylate polymer and copolymer additives. J Biomed Mater Res. 1993;27(3):367-377. [74]Grasel TG, Castner DG, Ratner BD, et al. Characterization of alkyl grafted polyurethane block copolymers by variable takeoff angle x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. JBiomed Mater Res. 1990;24(5):605-620. [75]Yu XH, Okkema AZ, Cooper SL. Synthesis and physical properties of poly(fluoroalkylether)urethanes. J Appl Polym Sci. 1990;41(7-8):1777-1795. [76]Yoon SC, Sung YK, Ratner BD. Surface and bulk structure of segmented poly(ether urethanes) with perfluoro chain extenders. 4. Role of hydrogen bonding on thermal transitions. Macromolecules. 1990;23(20):4351-4356. [77]Shin YC, Han DK, Kim YH, et al. Antithrombogenicity of hydrophilic polyurethane-hydrophobic polystyrene IPNs. II. In vitro and ex vivo studies. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 1994;6(3):281-296. [78]Matthews KH, Kodama M. The effect of microphase separated structures on the blood contacting properties of a series of linear segmented poly(etherurethaneurea) elastomers. Mater Sci Eng C Biom Mater Sensor Sys. 1994;2(1-2):51-59. [79]Tingey KG, Andrade JD. Probing surface microheterogeneity of poly(Ether Urethanes) in an aqueous environment. Langmuir. 1991;7(11):2471-2478. [80]Stauffer SR, Peppas NA. Poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels prepared by freezing-thawing cyclic processing. Polymer. 1992;33(18):3932-3936. [81]Gu YJ, Inoue K, Shinohara S, et al. Xenotransplantation of bioartificial pancreas using a mesh-reinforced polyvinyl alcohol bag. Cell Transplant. 1994;3(Suppl 1):s19-21. [82]Fujimoto K, Minato M,Ikada Y. Poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels prepared under different annealing conditions and their interactions with blood components. ACS Symp Ser. 1994;540(Chapter 20):228-242. [83]Chaikof EF, Merrill EW, Callow AD, et al. PEO enhancement of platelet deposition, fibrinogen deposition, and complement C3 activation.J Biomed Mater Res. 1992;26(9):1163-1168. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||